Multiple Choice Question (MCQ)
If \cos A + 2\cos B + \cos C = 2 then a, b, c are in
-
✓
2b=a+c
-
×
b^2=ac
-
×
a=b=c
-
×
None of these
If \cos A + 2\cos B + \cos C = 2 then a, b, c are in
2b=a+c
b^2=ac
a=b=c
None of these
This method uses trigonometric identities and Helen’s Formula
Given \cos A + 2 \cos B + \cos C = 2
⇒ \cos A + \cos C = 2(1 – \cos B)
Using Sum to Product Identity
\cos \alpha + \cos \beta = 2\cos\dfrac{\alpha +\beta }{2} \cos\dfrac{\alpha -\beta }{2}
and Double angle identity
\cos2 \alpha = 1-2 \sin^2 \alpha
⇒ 2 \cos\dfrac{A+C}{2} \cdotp \cos\dfrac{A-C}{2} = 4 \sin^2(\dfrac{B}{2} )
Since the sum of the three internal angles is equal to \pi
\therefore \dfrac{A+C}{2} = \dfrac{\pi}{2}-\dfrac{B}{2}
⇒ 2 \sin\dfrac{B}{2}\cos\dfrac{A-C}{2} = 4\sin^2 \dfrac{B}{2}
⇒ \cos\dfrac{A-C}{2} – \cos\dfrac{A+C}{2} = \cos\dfrac{A+C}{2}
Using Helen formula
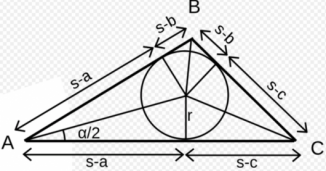
\because A =\dfrac{1}{2} (a+b+c)r
r = \dfrac{A}{s}
= \dfrac{ \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}}{s}
=\sqrt{\dfrac{(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}{s} }
in which A is the area of the triangle, s = \dfrac{a+b+c}{2}
\sin \dfrac{A}{2} =\dfrac{r}{\sqrt{r^2+(s-a)^2} }
=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+\dfrac{(s-a)^2}{r^2} } }
=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+\dfrac{s(s-a)}{(s-b)(s-c)} } }
=\dfrac{\sqrt{(s-b)(s-c)} }{\sqrt{s^2-(b+c)s+bc+s^2-sa}}
=\dfrac{\sqrt{(s-b)(s-c)} }{\sqrt{2s^2-(a+b+c)s+bc}}
=\dfrac{\sqrt{(s-b)(s-c)} }{\sqrt{bc}}
Similarly,
\sin \dfrac{B}{2} = \dfrac{\sqrt{(s-a)(s-c)} }{\sqrt{ac}}
\sin \dfrac{C}{2} = \dfrac{\sqrt{(s-a)(s-b)} }{\sqrt{ab}}
Substituting to (2) yields
⇒ 2(s – b) = b
⇒ a + b + c – 2b = b
⇒ a + c = 2b
This method uses trigonometric identities and the Law of Sines
Following (1) of the method 1
Multiplying 2\cos \dfrac{B}{2} with two sides of the equation
2\cos\dfrac{A-C}{2} \cos \dfrac{B}{2} = 2\cdotp 2\sin\dfrac{B}{2}\cos \dfrac{B}{2}
2\cos\dfrac{A-C}{2} \sin \dfrac{A+C}{2} = 2\cdotp 2\sin B
Using Product to sum identity,
\cos \alpha\sin \beta = \dfrac{1}{2} [\sin(\alpha+\beta ) - \sin(\alpha - \beta) ]
Using the Law of Sines,
\sin A=\dfrac{a}{2R}
\sin B=\dfrac{b}{2R}
\sin C=\dfrac{c}{2R}
Substituting to (2) yields
2b=a+c